
Spending quality bonding time with grandparents can create lasting memories and strengthen family connections. It is always helpful to be patient, mindful, and attentive when spending time with the grandparents, as it may take a little extra effort to accommodate their pace and preferences. The key is to create an atmosphere of love, respect, and connection during your time together. And what better way to celebrate this special day than by gathering together or spending a cozy day indoors? There's nothing quite like the joy of sharing stories and laughter over a game!
Storytelling and Reminiscing: Sit down with your grandparents and ask them to share stories from their past. This can be a great way to learn about their life experiences, family history, and the world from the lens of their youth. It will take you back in time and help you visualize a different world from the one you see today! Ask for their opinion about the changed world and listen to them share their perspectives and feelings. You can also share your own stories, fostering a sense of connection across generations.
Engage in creative activities: Cooking or baking can be a wonderful way to bond. Ask your grandparents to teach you a family recipe or share their culinary skills with you. Not only will you create delicious meals or treats, but you can also learn about the secret ingredients they use to make lip-smacking dishes. You will also have fun working together in the kitchen! Activities like painting, knitting, or crafting can also be picked up based on your and your grandparent's shared interests. Many grandparents have artistic talents that they would love to share, as nothing gives them the utmost joy than watching their own grandchildren inculcate their techniques and strokes. Above all, working on a project together can be both enjoyable and educational!Games and Puzzles: Playing board games, card games, or working on puzzles together is entertaining and mentally stimulating. You can choose games like Monopoly Super E-Banking, Monopoly Deal Card Game, and Wordle that cater to various skill levels and preferences, ensuring everyone can participate. Such games foster a sense of connection with one another and create trust. You experience the unrivaled satisfaction of engaging in laughter with your loved ones. It encourages familial ties and creates a safe space for emotional expression while playing alongside the elders of the family.Fun ways to make your grandparents feel special | MorungExpress | morungexpress.com
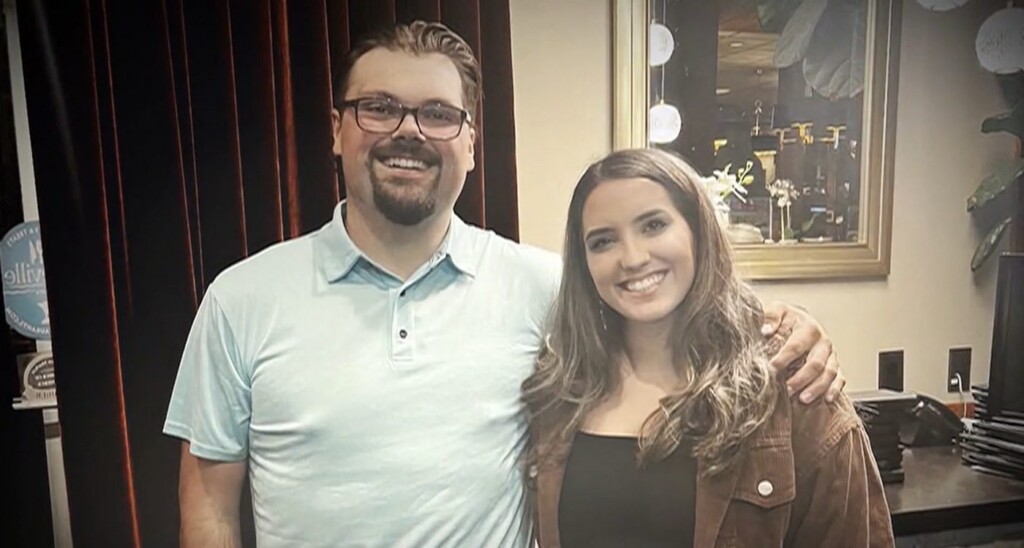
 Zach Zarembinski and Isabelle Richards – credit, family photo
Zach Zarembinski and Isabelle Richards – credit, family photo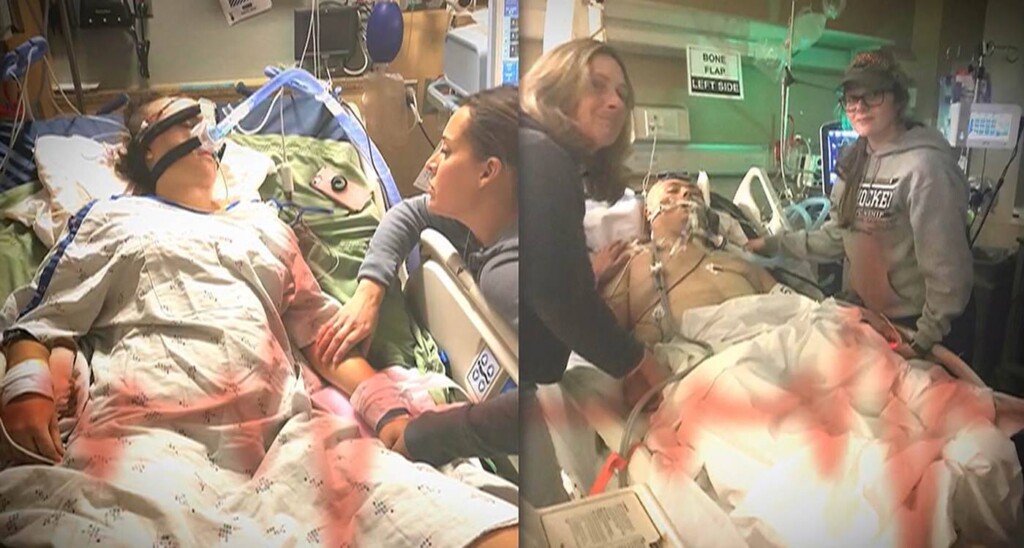 credit – family photo
credit – family photo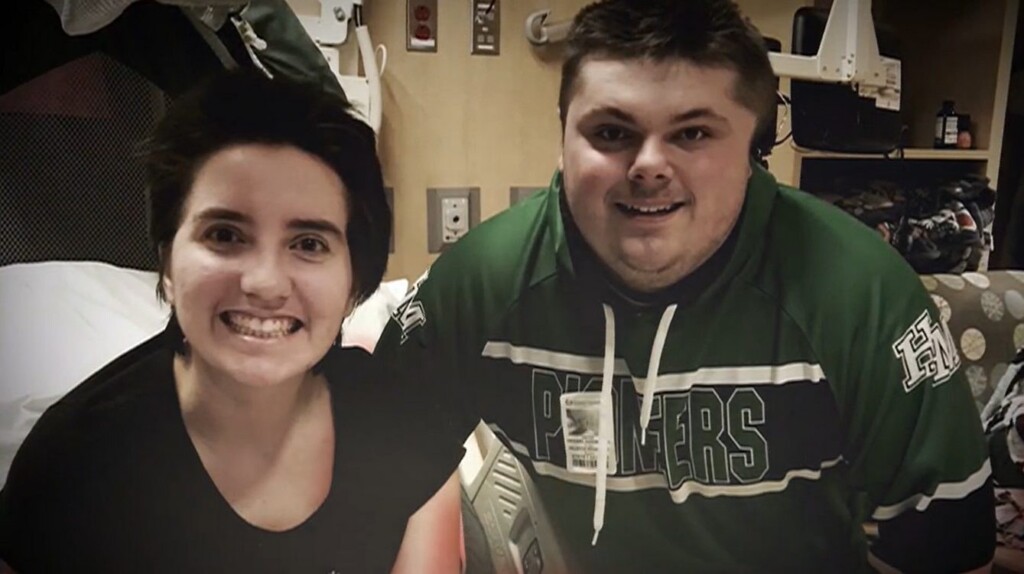 Zach and Isabelle after they’d both woken up – credit family photo
Zach and Isabelle after they’d both woken up – credit family photo